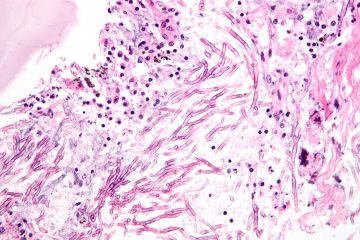
Fungal Infections
First WHO-led global initiative to systematically prioritize fungal pathogens
Fungal infections cause major morbidity and mortality in healthcare systems worldwide. According to the Global Action for Fungal Infections (GAFFI), 300 million people worldwide suffer from a serious fungal infection each year, with over 1.5 million of them dying from their infection. Nevertheless, in many places around the world, the prevalence and true burden of these diseases is unknown. Moreover, clinicians find very few treatment options for their patients. As a result, endemic regions and Read more…